
Accidentally eating gluten is a major concern for those with celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), or anyone avoiding gluten for health reasons. Gluten-digesting enzymes aren’t a free pass to eat gluten, but they can help manage trace amounts from cross-contamination or hidden sources. This blog covers how gluten-digesting enzymes work, when they may be helpful, and what the research says about leading options.
What Are Gluten-Digesting Enzymes?
These supplements contain specialized enzymes that target proline- and glutamine-rich peptides in gluten—particularly gliadin and glutenin—which resist normal digestion due to their unique structure. Enzymes like dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV), Tolerase®G, and Glutalytic® can break these peptides into smaller, less immunogenic fragments.
Wondering how gluten affects your brain and mood? Read “Gluten & Brain Health: Brain Fog, Mood and Fatigue” for the full story.
Important: These enzymes are designed for accidental gluten exposure, not intentional consumption, especially for those with celiac disease, where even small amounts can cause damage. A 2017 study warns that many commercial glutenases lack evidence for fully neutralizing gluten, so they’re not a substitute for a strict gluten-free diet [1].
When to Take Gluten Enzymes
To maximize effectiveness, take 1–2 capsules just before meals that may contain hidden gluten, such as:
- Dining out or ordering takeout
- Restaurant meals with unclear ingredient sourcing
- Meals with grains or processed foods
- During food reintroductions
- Meals with multiple allergens (e.g., dairy, soy, egg, corn)
Timing is key, as enzymes need to act in the stomach before gluten reaches the small intestine, where it can trigger immune responses in celiac disease or NCGS.
How Gluten Digestive Enzymes Work
DPP-IV (Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV)
- Function: An exopeptidase that breaks down gluten fragments at one end of the protein chain
- Limitations: Effective only at neutral pH (intestine, not stomach) and has limited gluten-degrading capacity alone. A 2001 study showed DPP-IV works best synergistically with other proteases [2].
Tolerase®G (Prolyl Endopeptidase)
- Source: Derived from Aspergillus niger
- Function: Designed to break down tough, gluten protein fragments in the stomach’s acidic environment (~pH 3–4), helping reduce potential reactions from accidental exposure [3].
- Supported by human clinical trials
Glutalytic®
- Source: A proprietary enzyme blend designed specifically to target gluten.
- Function: Works in a two-step process:
- Stage 1: Endopeptidases cut gluten proteins into smaller fragments.
- Stage 2: Exopeptidases further break these fragments down into pieces that are less likely to trigger an immune response.
- Evidence: Small, unpublished clinical trials showed that Glutalytic® reduced symptoms such as bloating and abdominal pain in non-celiac individuals eating gluten. It was also linked to lower levels of an antibody (deamidated gliadin IgA) that signals immune reactivity to gluten.
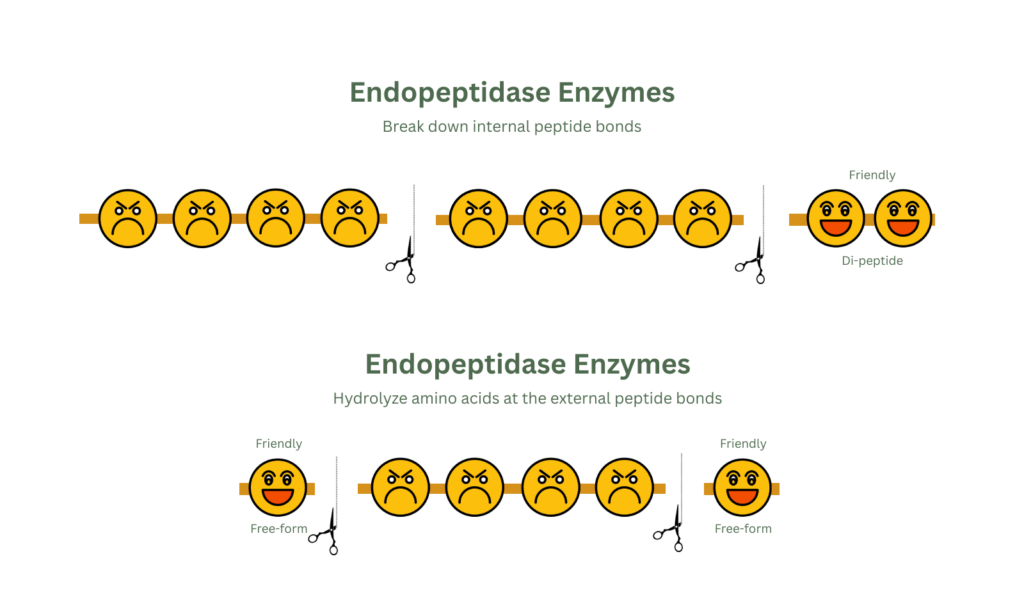
Can Glutalytic® Help with Other Common Allergens?
While Glutalytic® is primarily designed to help break down gluten, its dual-action proteolytic activity may also assist in digesting other difficult-to-break-down food proteins. This includes proteins in milk, soy, eggs, nuts, fish, and shellfish, which are all common triggers for food sensitivities.
Some research also suggests these enzymes may help with other hard-to-digest compounds, such as Bt toxins in GMO foods.
Note: Enzyme supplements are not a substitute for strict avoidance in people with diagnosed food allergies, especially IgE-mediated reactions that can cause serious or life-threatening responses. However, they may support digestion and help reduce the overall immune burden from accidental exposures or non-IgE food sensitivities.
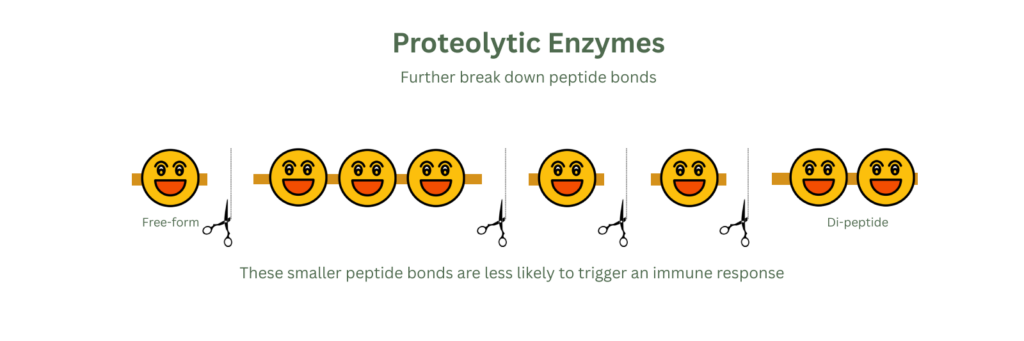
Proteolytic Enzymes
- Examples: Peptidase, bromelain, papain.
- Function:: Broadly break down proteins (including gluten) → may reduce immune-reactive fragments
- Evidence:: A 2025 review highlights that microbial peptidases, including proline-specific ones, are promising for degrading immunogenic gluten peptides, though more in vivo studies are needed [4].
How to Choose the Right Product
- Targets both gliadin and glutenin (the two main components of gluten).
- Example: enzymes that combine DPP-IV with other proteases.
- Formulas that combine DPP-IV with endopeptidases work more effectively than single enzymes.
- Additional proteolytic enzymes (like peptidase, bromelain, or papain) help ensure broader protein breakdown.
- Avoid fillers or additives containing gluten, soy, or dairy.
- Choose practitioner-trusted formulas with research or clinical validation to support their effectiveness.
Top Gluten-Digesting Enzyme Products
Who Should Use Gluten Enzymes (and Who Shouldn’t)
Helpful for:
- Reducing risk from cross-contamination
- Dining out, traveling, or uncertain ingredient lists
- Supporting cautious reintroduction phases of foods (while still strictly avoiding gluten).
Not for:
- Intentional gluten consumption with celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity or wheat allergy
- Children with IgE allergies
- As a substitute for a strict gluten-free diet
Final Thoughts
Gluten-digesting enzymes can provide an extra layer of protection for accidental gluten exposure, reducing the immune burden and supporting gut health. However, they’re not a free pass, cure or a substitute for a gluten-free diet.
Work with a functional medicine practitioner for personalized testing and guidance to choose the right enzyme for your needs.
If you’d like personalized guidance, functional testing, or support in choosing the right gluten-digesting enzymes, please reach out I’d be happy to provide expert recommendations tailored to your unique needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best enzyme to digest gluten?
The most studied gluten-digesting enzymes are DPP-IV, Tolerase®G, and Glutalytic®. Each targets different parts of gluten proteins and may be combined for optimal results.
Can digestive enzymes help with celiac disease?
No, they’re not a treatment for celiac disease or a substitute for a gluten-free diet in those with celiac disease. They are only intended for accidental exposure and do not prevent intestinal damage from intentional gluten intake.
When should I take gluten-digesting enzymes?
Take them right before meals that may contain hidden gluten, especially when dining out, during travel, or at social gatherings.
Do these enzymes work for dairy too?
Some gluten enzyme formulas also include enzymes like lactase or Dairylytic®, which help break down dairy proteins and lactose.
Where to Order Trusted Gluten-Digesting Enzymes
For best results, I recommend ordering from a professional-grade source. Supplements from third-party sites (like Amazon or eBay) may be expired, improperly stored, or counterfeit—unless sold directly by the manufacturer.
To ensure you receive clinically-tested, high-quality enzymes, order directly through my Fullscript Store. .
- Guaranteed quality, storage, and potency
- Practitioner-vetted brands
- Auto-refill and personalized protocols
- Access to client-only discounts
You deserve supplements you can trust. Used properly, they can help reduce the immune burden of accidental gluten exposure and give your gut some added support.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have a medical condition, food allergy, or take prescription medications. For individuals with celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, or food allergies, enzyme supplements are not a substitute for a strict gluten-free diet or allergen avoidance. Results may vary, and recommendations should be tailored to individual needs.
+ show Comments
- Hide Comments
add a comment